Applications
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) metabolomics is an exceedingly versatile analytical technique, offering a broad spectrum of applications by virtue of its capacity to non-invasively and comprehensively profile small molecules in biological samples.
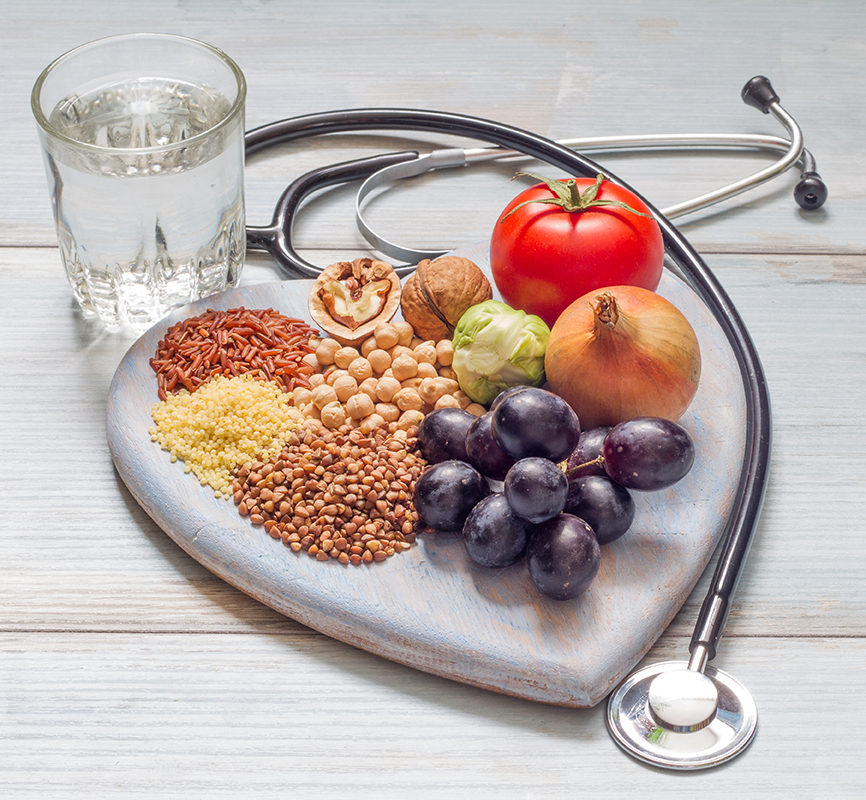
Beyond qualitative and quantitative metabolite analysis, it finds utility across a diverse range of biological matrices, encompassing biofluids, tissues, and cell extracts. Its versatility further encompasses the identification and quantification of established metabolites as well as the exploration of novel biomarkers or compounds. Its adaptability enables the handling of an extensive array of sample types, from intricate metabolic profiling in clinical and pharmaceutical research to the analysis of complex mixtures in environmental samples.
Finally, its non-destructive character and minimal sample preparation prerequisites render this technology an invaluable tool for investigating a wide spectrum of biological systems, thereby facilitating advancements in domains such as disease biomarker discovery, drug metabolism studies, and personalized medicine